Although the terms kW and kWh have similar names, they are entirely different. If you’ve only ever driven conventional fuel vehicles, we’re here to explain this basic EV knowledge today. To put it simply, a kW is a measure of power, and a kWh is a measure of energy; power is the rate at which something uses energy, and energy is the capacity to do work.
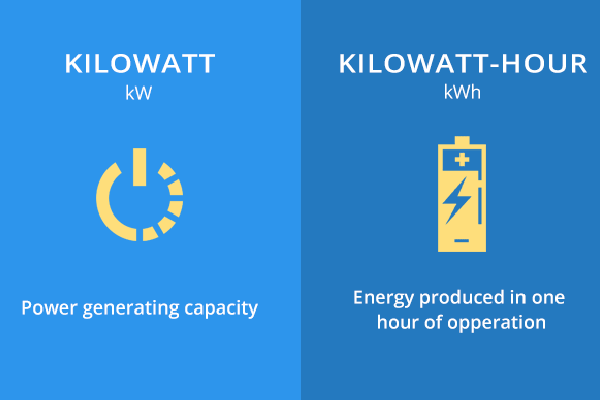
The Kilowatt
A kilowatt is simply a measure of how much power an electric appliance consumes—it’s 1,000 watts to be exact. You can quickly convert watts (W) to kilowatts (kW) by diving your wattage by 1,000:
1,000W 1,000 = 1 kW.
The Kilowatt-Hour
A kilowatt-hour or kWh is simply a measure of the energy consumed. From this abbreviation, the ‘k’ stands for kilo, which means 1000. The ‘W’ stands for watts – a unit of power, and the ‘h’ stands for an hour – a measure of time.
So, a kWh refers to the amount of 1000 watts of energy your household consumes per hour. The total output energy produced by a solar system, as well as the amount stored in solar batteries is measured this way.
To calculate the kWh your solar panel produces. Here’s a simple formula;
kWh = Total Watts x Time(hours)
What’s the difference between a kW and kWh?
For electric vehicles, a kilowatt is a rate at which the electric vehicle absorbs or outputs energy. And kWh refers to how much energy a vehicle can store.
When DC fast charging, the Ford F-150 Lightning, for instance, tops out at about 150 kilowatts. That’s the quickest rate this truck can absorb energy. In comparison, the Nissan Leaf hatchback tops out at just 100 kilowatts which is appreciably slower in this context. Think of kilowatts as a garden hose. The large larger the diameter, the more water can flow through at a given time.
At a public EV charging station, you’ll see kilowatt ratings displayed on the units themselves, and this helps you select the best charger for your EV while leaving more or less powerful chargers for other drivers. There’s no sense plugging your Nissan Leaf into a 350-kilowatt unit if the car can only take in 100.
Getting back to kilowatt hours, as mentioned, that term is used to describe energy storage, precisely the capacity of a vehicle’s battery pack. That is no different than the size of a conventional car or truck gas tank. If kilowatts is the diameter of the hose, then kilowatt hours is the bucket’s volume.
As you can see, there is a big difference between kilowatts and kilowatt hours. So, you will understand electric vehicles more clearly after reading this article.