The charging pile is a charging facility for “refueling” electric vehicles, and the scientific name is also called “off-board charger”. At present, charging piles are divided into AC charging piles and DC charging piles. This article will introduce the difference between AC charging piles and DC charging piles.
DC charging pile, commonly known as “fast charging”, is a power supply device that can provide DC power for off-board electric vehicle power batteries. The input voltage of the DC charging pile adopts three-phase four-wire AC380V±15%, the frequency is 50Hz, and the output is adjustable direct current, which directly charges the power battery of the electric vehicle. Since the DC charging pile adopts a three-phase four-wire system for power supply, it can provide sufficient power, and the output voltage and current adjustment range is large, which can meet the requirements 0f fast charging piles.

AC charging pile, commonly known as “slow charge”, is a power supply device that provides AC power for electric vehicle on-board chargers. The AC charging pile only provides power output and has no charging function. It needs to be connected to the on-board charger to charge the electric vehicle, which actually plays the role of controlling the power supply.
To put it simply, the AC charging pile needs to be charged with the help of the on-board charger, and the DC fast charging pile does not need this equipment. The charging speed of the two is quite different. It takes 8 hours for a pure electric vehicle (common battery capacity) to be fully discharged through an AC charging pile, while it only takes 2 to 3 hours to pass through a DC fast charging p
Generally speaking, the size of the DC charging pile is relatively large. This is because there needs to be an AC-to-DC power supply module inside, and the higher the charging power, the greater the number of modules, and the correspondingly larger the volume of the charging pile. At the same time, there are certain differences between the two in terms of power plugs. The DC charging pile is 9 holes, and the AC charging pile is 7 holes. This is also the most striking feature of the two. In addition, the DC charging pile is connected to a 380V high-voltage cable, while the AC charging pile is connected to a 220V household cable.
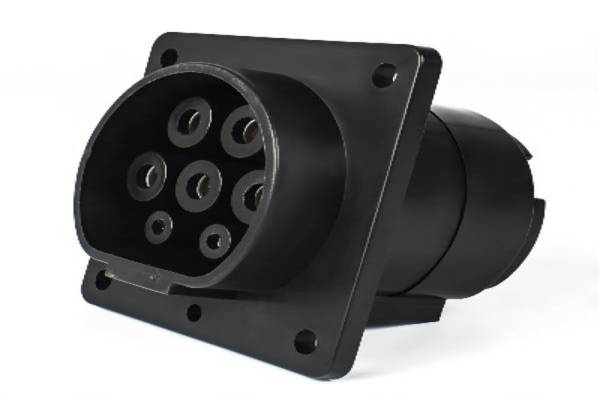

In terms of application scenarios, DC charging piles are more suitable for operational charging services, such as electric buses, electric taxis, electric logistics, electric special vehicles, electric network car-hailing, etc., but because the complexity of the two structures is too different , the manufacturing cost of DC charging piles will be even higher, so the price of today’s DC charging piles will be significantly higher than that of AC charging piles.
In terms of practicality, if it is only placed in a general parking space or at home, the AC charging pile can meet the requirements. In addition, for DC charging piles, because the current and voltage required are relatively large, ordinary household circuits cannot bear it at all, so it is not realistic to install fast charging piles at home.