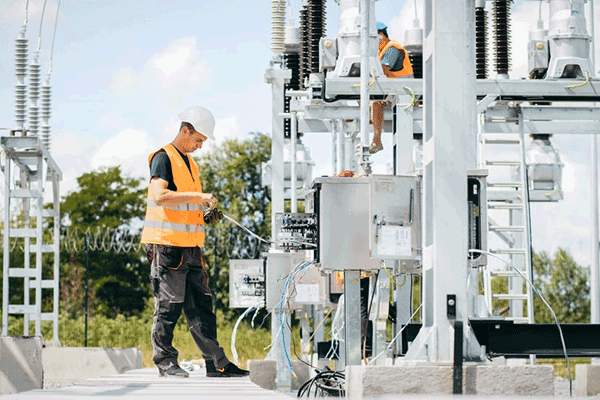
1. How Much Power Do You Need?
First and foremost, you need to ascertain the amount of power required at the site. This depends on the number of DC and AC chargers you plan to install and their capacity. DC chargers provide a higher amount of power to electric vehicles, hence requiring more from the grid. To ensure the grid can meet your demands, you’ll need to evaluate the expected EV traffic and their charging behaviors, such as peak charging times and duration of charges.
2. Is There Local Grid Supply Competition?
The competition for grid supply isn’t just from other DC fast-charging companies. In many places, as electric vehicles become more common, the demand on the grid is increasing. Thus, you might find yourself competing with other businesses like factories, commercial centers, or residential areas for grid supply. To ensure a steady power supply, understanding local electrification plans and other potential large-scale projects is crucial.
3. How to Choose the Location of the DC Fast Charging Station Based on Grid Connectivity?
Choosing the right site location is a complex process that involves multiple factors. Apart from considering the available grid capacity of a given substation and its distance from the proposed site, other factors like terrain, soil type, traffic flow, etc., come into play. All these influence the cost and complexity of the grid connection.
4. Costs and Budgeting
The financial aspect of grid connection is a significant consideration, encompassing various facets:
- Connection Fees: This is the initial cost associated with establishing a grid connection with the power company. It might include engineering fees, material costs, and other related expenses.
- Usage Charges: These are the ongoing costs you pay for drawing power from the grid. It might be based on your actual consumption or a reserved capacity.
- Demand Charges: In some regions, you might incur additional charges if your consumption exceeds a certain threshold.
- Potential Subsidies: Some governments or institutions might offer subsidies or incentives to encourage the establishment of EV charging stations. Being aware of these opportunities can help in cost savings.
5. Future Scalability
With the growth of the EV market, considering the scalability of the charging station becomes paramount:
- Grid Capacity: Ensure that your grid connection has ample capacity to cater to future demands. This might mean collaborating with the power company to reserve more capacity or pre-planning expansions.
- Site Size: Opt for a location that can accommodate more chargers or can be easily expanded upon.
- Technological Upgrades: As technology advances, new charging technologies and standards might emerge. Ensure that your site can be easily upgraded technologically.
6. Safety and Compliance
Ensuring the safety and compliance of the grid connection and the charging station is crucial:
- Local and National Standards: Stay compliant with local and national power and construction standards. This might encompass electrical safety, building codes, and environmental considerations.
- Safety Equipment: Ensure all chargers and related equipment are equipped with necessary safety devices like circuit breakers, grounding devices, and fire prevention equipment.
- Training and Education: Provide appropriate training to your staff, ensuring they know how to operate and maintain the charging station safely.