Lufthansa, ETH Zürich, Climeworks & Synhelion to cooperate on Sustainable Aviation Fuels; CO2 capture & solar thermochemical conversion
Green Car Congress
MAY 30, 2020
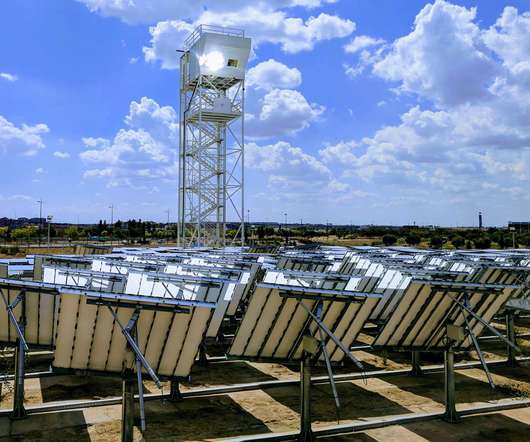
The researchers and engineers at ETH Zurich have developed innovative processes that make it possible to extract CO 2 from the atmosphere and, together with water and with the help of concentrated sunlight, convert it into a synthesis gas that can be used to produce jet fuel.







































Let's personalize your content