For companies that invest in EV charging, deploying battery storage can reduce power demand charges. Charging on demand is a tricky part of EV charging station operation. So do you know what a demand charge is? This article can answer all your doubts.
Energy Consumption
To understand “demand”, we have to start with what your energy bill tells you. Typically, there are three parts to commercial energy bills:
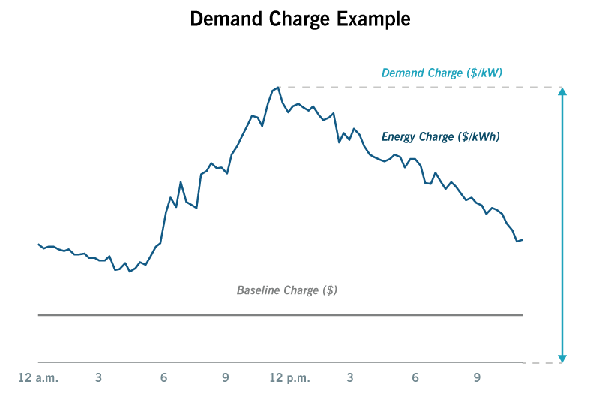
1. Baseline Charges
Often known as the connection fee. This is typically a set fee that everyone pays just to be part of the grid.
2. Energy or Usage Charges
This is the first load factor and reflects the quantity of what you use and when you use it. While energy usage can appear flat or in tiers (meaning the more energy you use, the higher the tier and charges), many utilities align energy charges to reflect Time of Use (TOU) for their commercial customers. A TOU schedule, which means energy consumed during peak energy demand hours will be more expensive and less expensive during low demand periods, is also becoming more commonly applied to previously flat or tiered energy charges.
TOU rate structures are more common for commercial customers, but are now rolling out to residential customers in states like California. In California and other areas of higher solar renewable energy penetration, supply and demand have shifted from midday as most expensive energy to early evenings when the sun doesn’t shine. Many western utilities have shifted their electricity peak hours and most expensive Usage Charges to cost the most on weekdays starting around 4:00 p.m. until as late as 9:00 p.m.
3. Demand Charges
The cost line that generates the most customer questions is demand charges, which is calculated on top of baseline and Energy or Usage. Demand is the hardest to conceptualize and one that most don’t pay attention to. It is a combination of how much electricity used and the rate at which it is consumed. Imagine how different watering your lawn would be using a standard garden hose on “gentle rain” nozzle setting versus a fire hose set on high. Then imagine everyone around you all using their fire hoses at the same time. That is demand.
What are demand charges?
Demand charges reflect the maximum amount of electricity a customer uses during a specific time interval (typically 15 minutes). These apply primarily to commercial customers rather than residential customers, as they usually generate higher electricity demand during peak hours. While each business can have its specific billing process, they will typically state the maximum electricity demand allocated to the customer. If that amount is exceeded over a more extended time, the business may charge the customer’s bill an on-demand fee. There are also various types of on-demand charges. For example, charges will increase during peak demand hours and decrease during off-peak demand hours.
The impact of ev charging on demand charges
Your peak demand usage will increase with the rated output of the charger. For example, if you install a 100kW DC fast charger, your peak demand will increase by 100kW when it starts working. If your business charges $30 per kW per month for demand, you will pay an additional $3,000 per billing cycle. Of course, if you install a higher power charger or have a more significant number of chargers, the demand charge will increase accordingly.
How Battery Energy Storage Reduces Demand Charges?
As you can see in the typical commercial power load curve below, the company starts operating at around 6:00 a.m. and closes at 9:00 p.m. The load profile includes all electrical loads, such as lighting, air conditioning, etc. You can see the demand charges start to come into play, along with the peaks in the load profile. These spikes represent the 150kW DC fast charger in use, which means the short frequency of use of the charger, with electric cars pulling up to charge and then leaving.
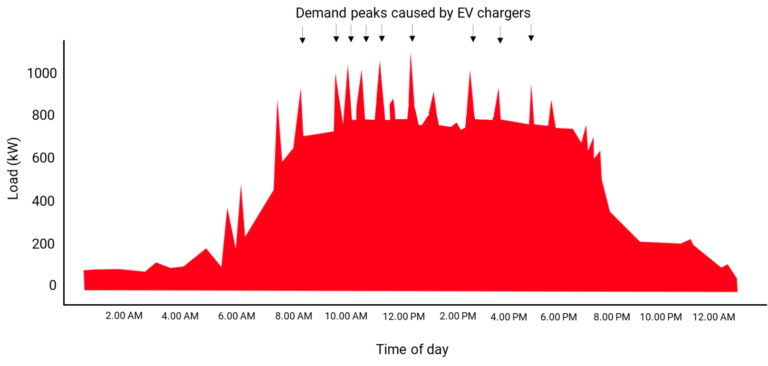
The graph below clearly shows the impact of battery storage on demand. As battery storage increases, peak demand peaks are smoothed out, directly reducing demand charges. We charge the batteries from the grid during off-peak hours because it does not increase the overall demand charge. The stored power is then used to power the EV charger during peak periods. Battery storage eliminates the peaks caused by EV charging and recharges the batteries at night.
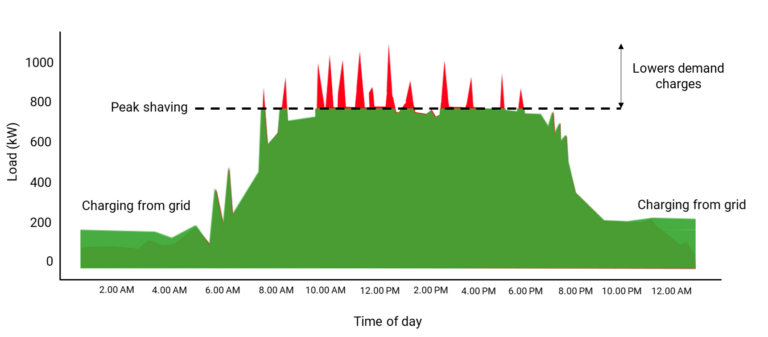
So we know that EV charging stations will increase the overall demand charges, but we also see that in many states, the amount charged per kW for demand charges by utilities is rising. As commercial customers can reduce their utility bills by utilizing on-site solar to reduce energy consumption charges (kWh), utilities are putting more of their fees into the demand for power as they align electric load profiles with the cost of the infrastructure. In some cases in the US, we see 3 – 5% increases in demand charges annually, but in some states, some utility companies are increasing demand charges much faster. The increasing costs for demand charges make battery energy storage an even more attractive option to combine with your electric vehicle charging implementation.
How will SETEC POWER help you?
As we’ve discussed, combining your EV charging with battery storage makes sense. SETEC POWER has introduced the Emergency mobile EV charging system for this purpose, which allows you to store energy and provide attractive mobile charging services. Combined with your local government incentives, this will further reduce the total cost of ownership and will be the most cost-effective and efficient solution.