Israeli startup Electreon is testing dynamic wireless charging on a short bus route in Tel Aviv, allowing an electric bus to recharge as it drives along a stretch of road.
Electreon has electrified a roughly 700-meter (0.4-mile) section of a 2.0-kilometer (1.2-mile) route, and installed a static wireless charging station at the Tel Aviv University bus terminal, allowing the test bus to charge while boarding passengers, according to a company press release.
The charging system consists of coils embedded in the road, which can be connected to the grid as a source of electricity. The bus draws current from the coils using onboard receivers.
Electreon said the initial test phase, which focused on the reliability of the coils and their associated monitoring system, has been completed. Additional testing under different operating conditions—such as different loads and operating frequency—will come next, the company said. Eventually, Electreon expects the wirelessly charged bus to go into regular service for students of Tel Aviv University.
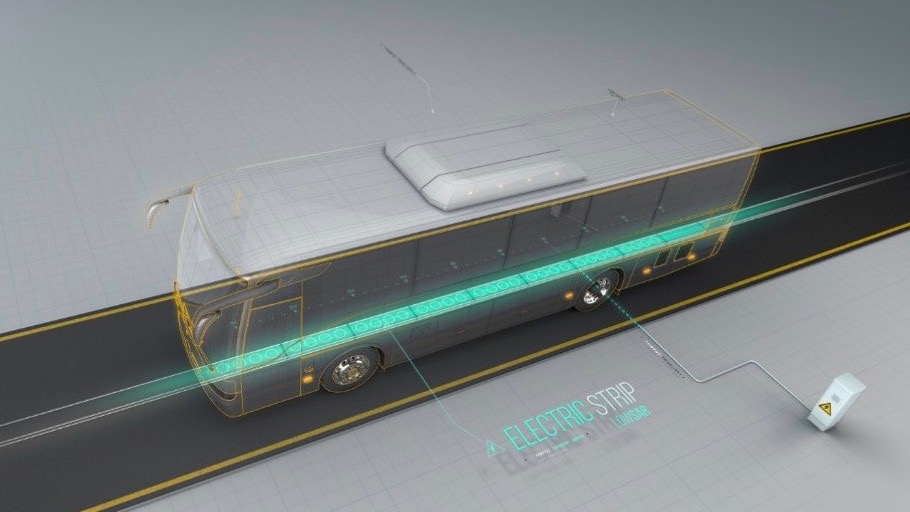
Electreon dynamic wireless charging
This isn't the first real-world test of Electreon's tech. The company previously installed wireless-charging hardware on a short section of Swedish road, and used it to charge electric trucks.
In 2017, Qualcomm demonstrated a system that charged a small van as it traveled at 60 mph. That technology was part of a 2019 deal selling Qualcomm's wireless-charging tech to WiTricity.
Although the standards for static wireless charging were harmonized last year, dynamic wireless charging remains a farther-off tech. A similar process of harmonization will be needed to ensure of interoperability of vehicles and charging hardware, but the tech shows a lot of promise.
Electreon noted that its dynamic wireless charging system doesn't take up space like conventional charging stations, or the overhead wires used by current trolley buses. Patches of dynamic wireless charging could help ease the load off other charging infrastructure, especially in fleet applications where multiple vehicles may have the same cycles of service and downtime.











